P R I N T I N G
Printing can be
carried out by a number of different processes. Regardless of the process used, the product
can be classified by the type of printing required.
1.
Monochrome
Where
only a single colour of printing ink is used. E.g. black & white,
sepia.
This type of printing
is often done using coloured paper/ card as this is a cheaper method of giving
the impression that more than one ink colour is used. Monochrome is obviously the cheapest form of
printing.
2.
Colour Printing
There are two main
types of colour printing.
(a)
Four-colour Process Printing
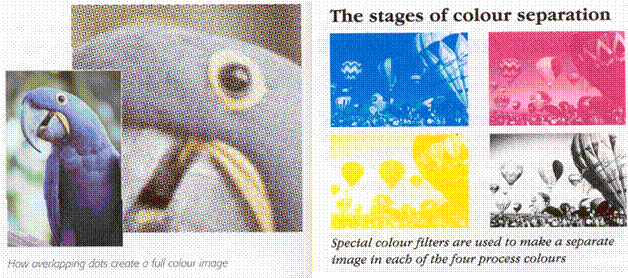
Also known as full colour
printing. The coloured image
is achieved by overlaying dots of four process colours; namely, cyan (blue), magenta (red), yellow
and black (CMYK), to give the illusion of a colour image. A separate printing plate has to be made up
for each of the four colours as part of a process called colour separation.
(b)
Spot Colours
This process is used where specific colours are
required in quantity. It is often used
in conjunction with full colour printing.
Individual colours are mixed prior to printing. This is a particularly common process where
special inks are used such as metallic or clear varnish (spot varnishing).
Checking for Quality
Registration marks are
used to make sure that the printing plates align properly. If they do not the image will appear blurred
and out of focus.
Colour quality is checked using colour
bars, where the density of colour is measured using a device called a colour densiometer.
![]()
Registration mark Colour Bars
Use the Printing Glossary resource to help you answer the following questions. (T:designtech:Graphics GCSE:General:Printing Glossary)
1)
Why
is it important to print a proof copy of a graphic product prior to
the main manufacturing run?
2)
Why
is the halftone method so useful in monochrome printing?
3)
Describe,
in a single sentence, what a scanner does.
4)
What
does a web mean in relation to printing?
5)
What
is imposition and give an example of where it
could be used.
6)
Why
are graphic products printed with a bleed
area?
7)
What
does the ISO standard mean in relation to paper
sizes?
8)
What
does gsm stand for?
9)
What
does the word register mean in relation to graphic
products?
10) What is the difference between perfecting and perfect binding?