1: Blood Circulation System
By the end of the session you will understand:
- the structure and circulation of blood
- the structure and circulation of blood vessels
- the structure and circulation of the heart
Components of blood
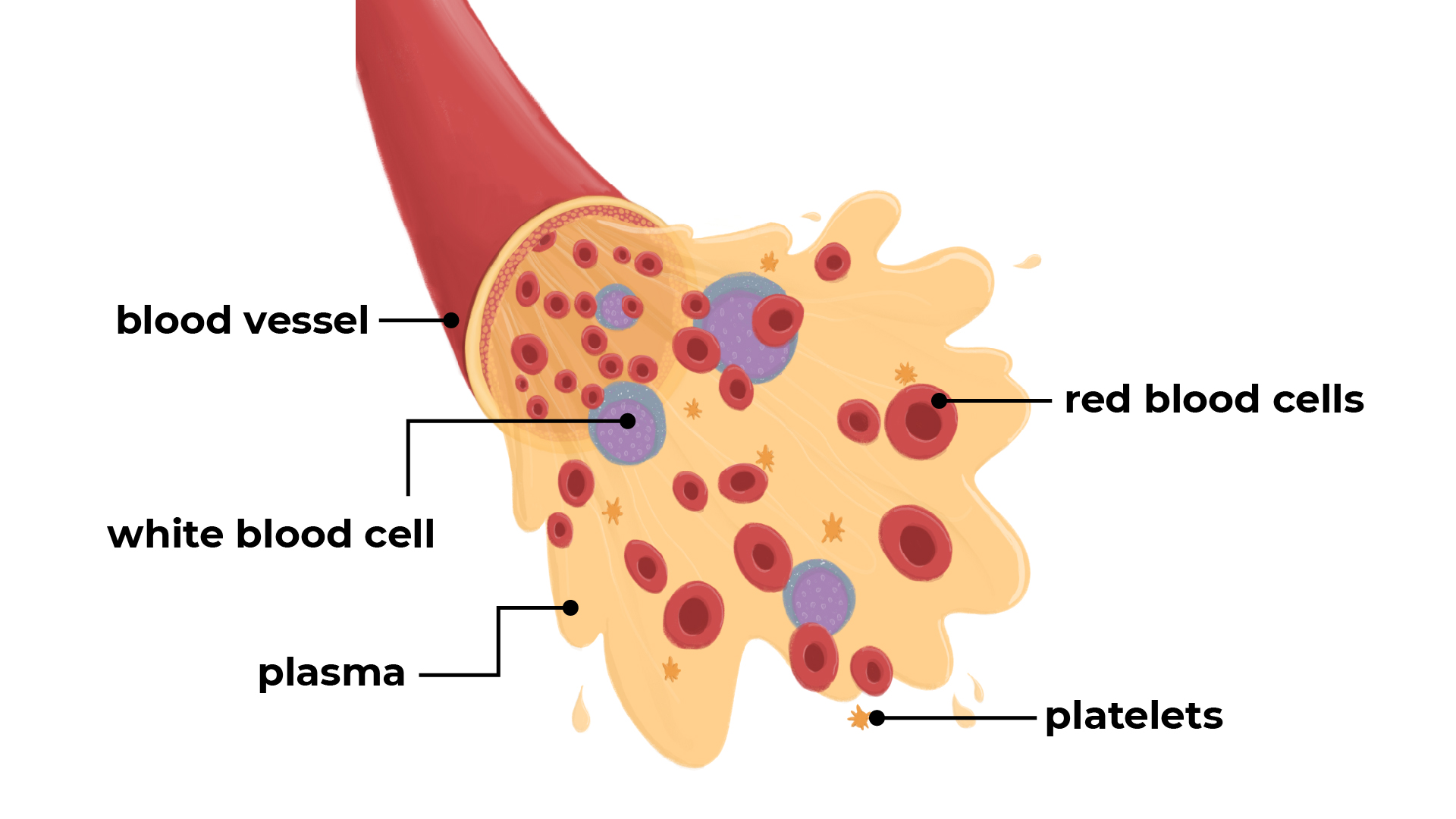
Split the class into groups of 4. Group decides who is 1, 2, 3 and 4.
Individuals become experts on 1-4 below, read through the extract, then report back to the rest of the group one at a time – others need to take notes as they report back.
1: Red Blood Cells
These cells carry oxygen around the body.
They are flattened, biconcave, disc-shaped cells; they are red in colour because of a pigment called haemoglobin. This joins with oxygen to transport it around the body. Red blood cells don't have a nucleus.
Iron is needed to produce haemoglobin. If there is a shortage of iron a person won't have enough red blood cells, this is called anaemia, less oxygen will be carried around the body.

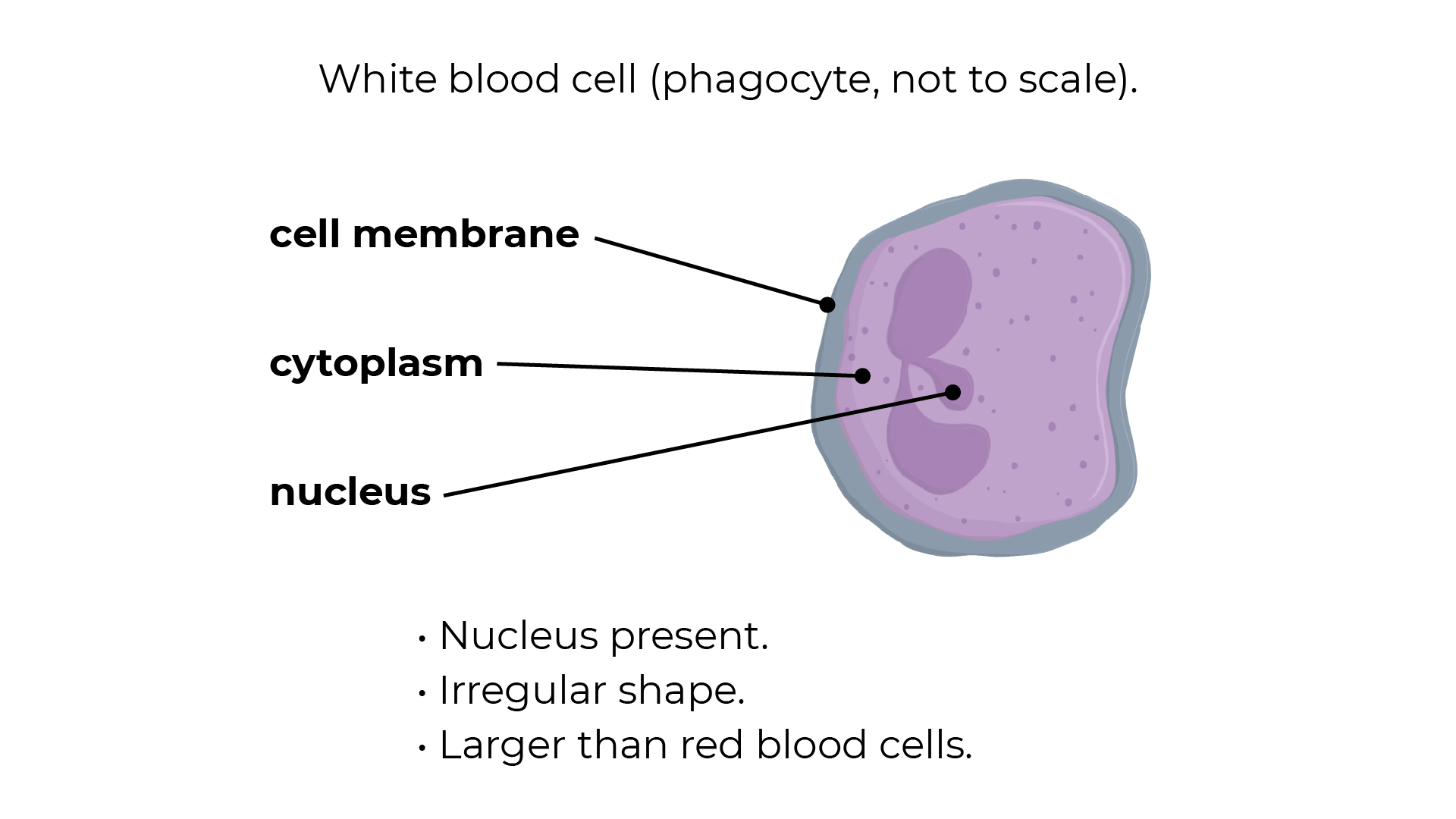
2: White Blood Cells
These cells defend the body against pathogens (microbes that cause disease).
They are bigger than red blood cells, and have a nucleus, but don't contain a pigment so are colourless.
If you have an infection the number of white blood cells in you body increases rapidly.
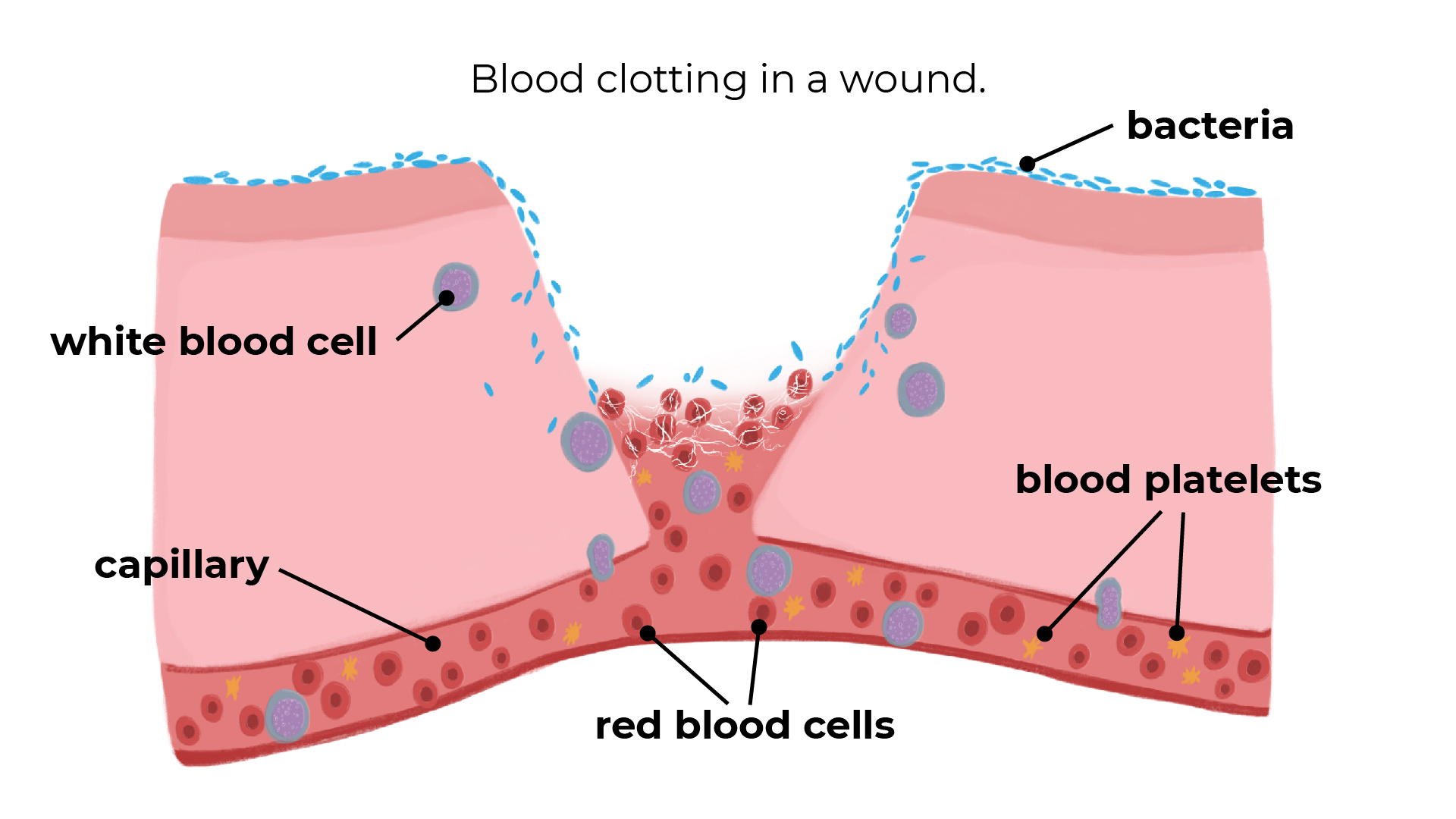
3: Platelets
Platelets clot the blood.
When the skin is cut you bleed. Platelets make the blood clot, forming a thick jelly. This hardens to form a scab, preventing bleeding and blood loss. The scab keeps the wound clean as new skin grows underneath.
This prevents pathogens from entering the body and bacterial infection.
4: Plasma
Plasma carries dissolved substances.
This is the liquid part of blood. It is pale yellow in colour and is 90% water.
Plasma carries many dissolved substances around the body:
- Small soluble food molecules, e.g. glucose, amino acids, etc.
- Waste chemicals produced by the body, e.g. carbon dioxide from respiration and urea produced by the liver.
- Hormones carried from the endocrine glands to their target organs, e.g. insulin.
- Mineral salts, e.g. sodium ions.
Plasma also distributes heat around the body.
Blood Vessels
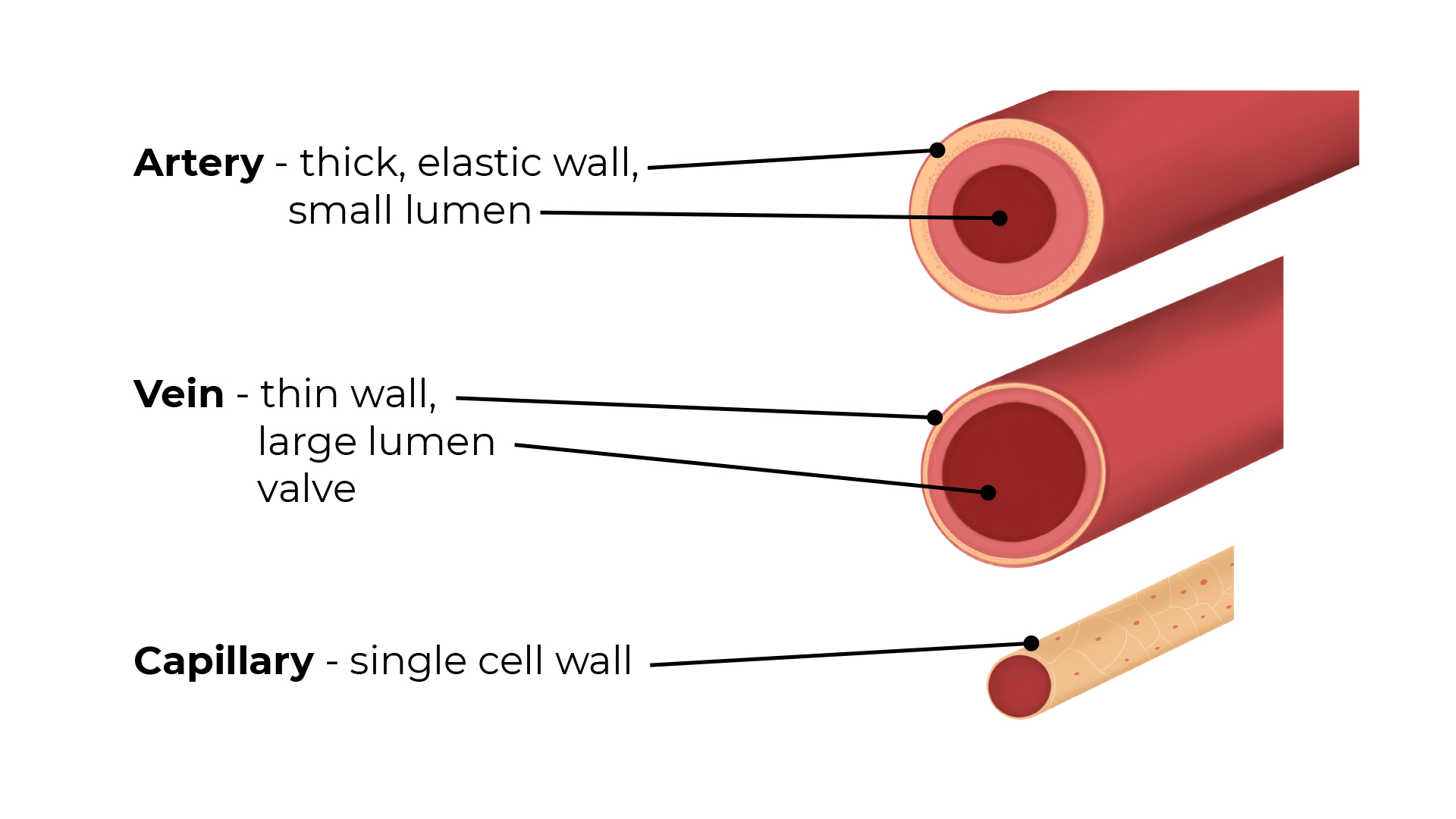
Blood Vessels

Use the information on the following slides to complete the grid in the worksheet.
Download Worksheet - Word, PDF
- Function of the blood vessel?
- From where and to where does the blood vessel transport blood?
- Adaptations – how has the blood vessel adapted for its role in the body?
You should label on the diagram...tough outer coat, muscle layer, endothelium and lumen.
Arteries
- Carry blood away from the heart (always oxygenated apart from the pulmonary artery which goes to the lungs)
- Have thick muscular walls
- Have small passageways for blood (internal lumen)
- Contain blood under high pressure
Veins
- Carry blood to the heart (always deoxygenated, apart from the pulmonary vein which goes from the lungs to the heart)
- Have thin walls
- Have larger internal lumen
- Contain blood under low pressure
- Have valves to prevent blood flowing backwards
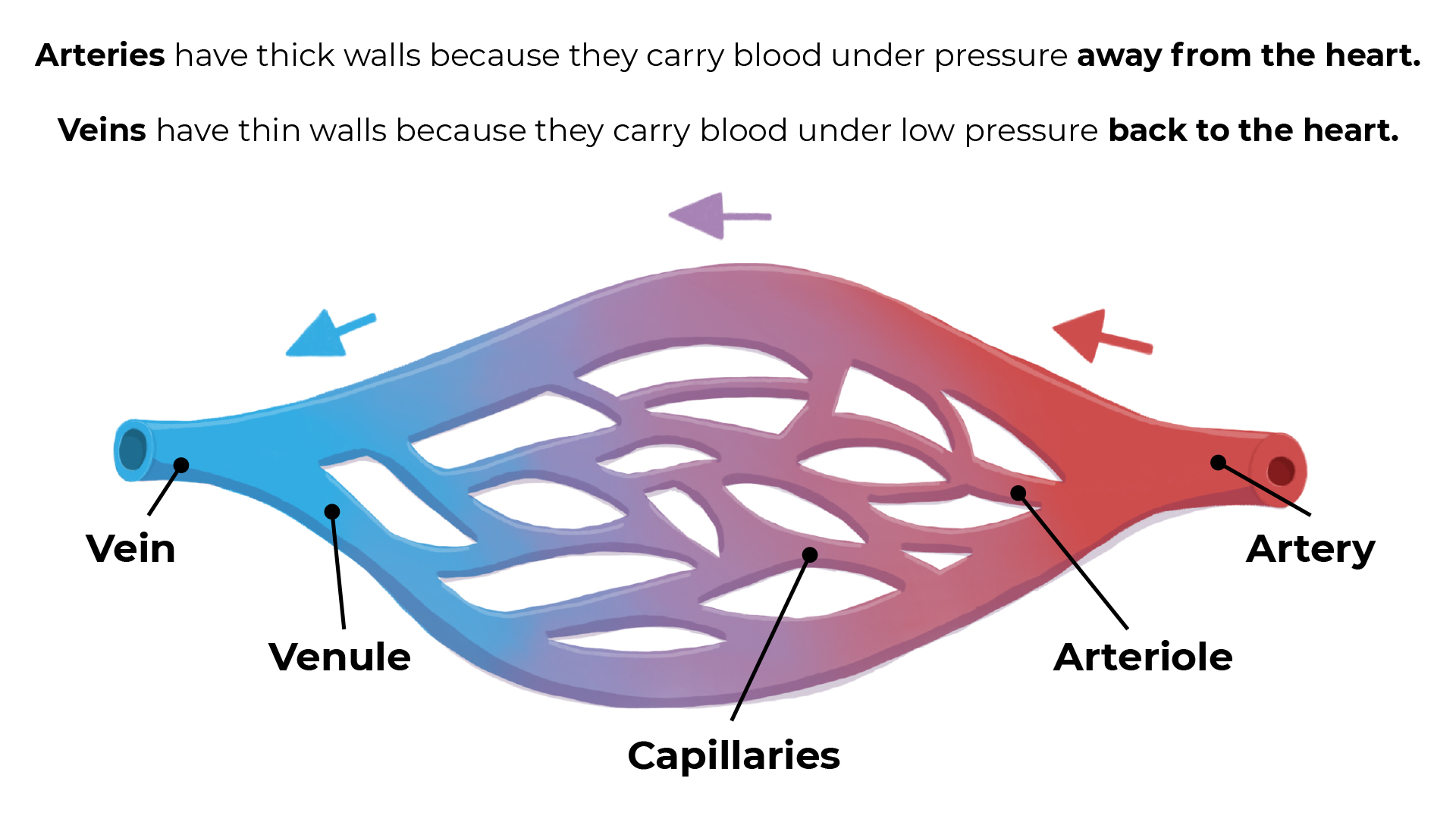
Capillaries
- Found in the muscles and lungs
- Microscopic – one cell thick
- Very low blood pressure
- Where gas exchange takes place. Oxygen passes through the capillary wall and into the tissues, carbon dioxide passes from the tissues into the blood.
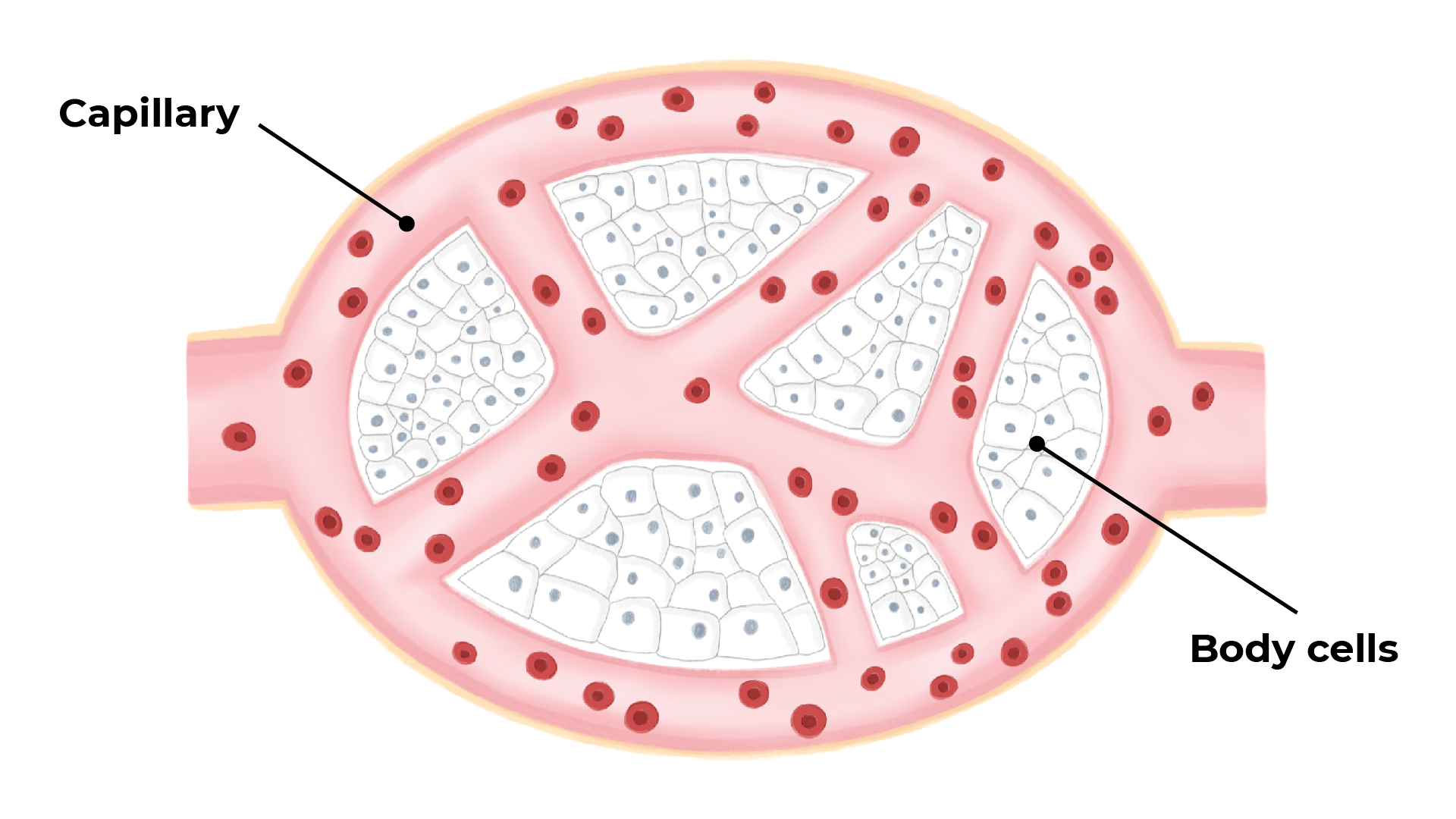
Capillaries are the smallest blood vessels that carry blood through the organs of the body. Substances needed by cells pass out of the blood to the tissues and substances produced by the cells pass into the blood through the walls of the capillaries.
- They form extensive networks so that no cell is far away from a capillary.
- Their walls are very thin to allow materials to diffuse easily between the blood and the body cells.
Double circulation: blood moves through the heart twice during one cycle/beat.
- 1. Pulmonary: From the heart to the lungs and back.
- 2. Systemic: From the heart to the body and back.

Parts of a heart
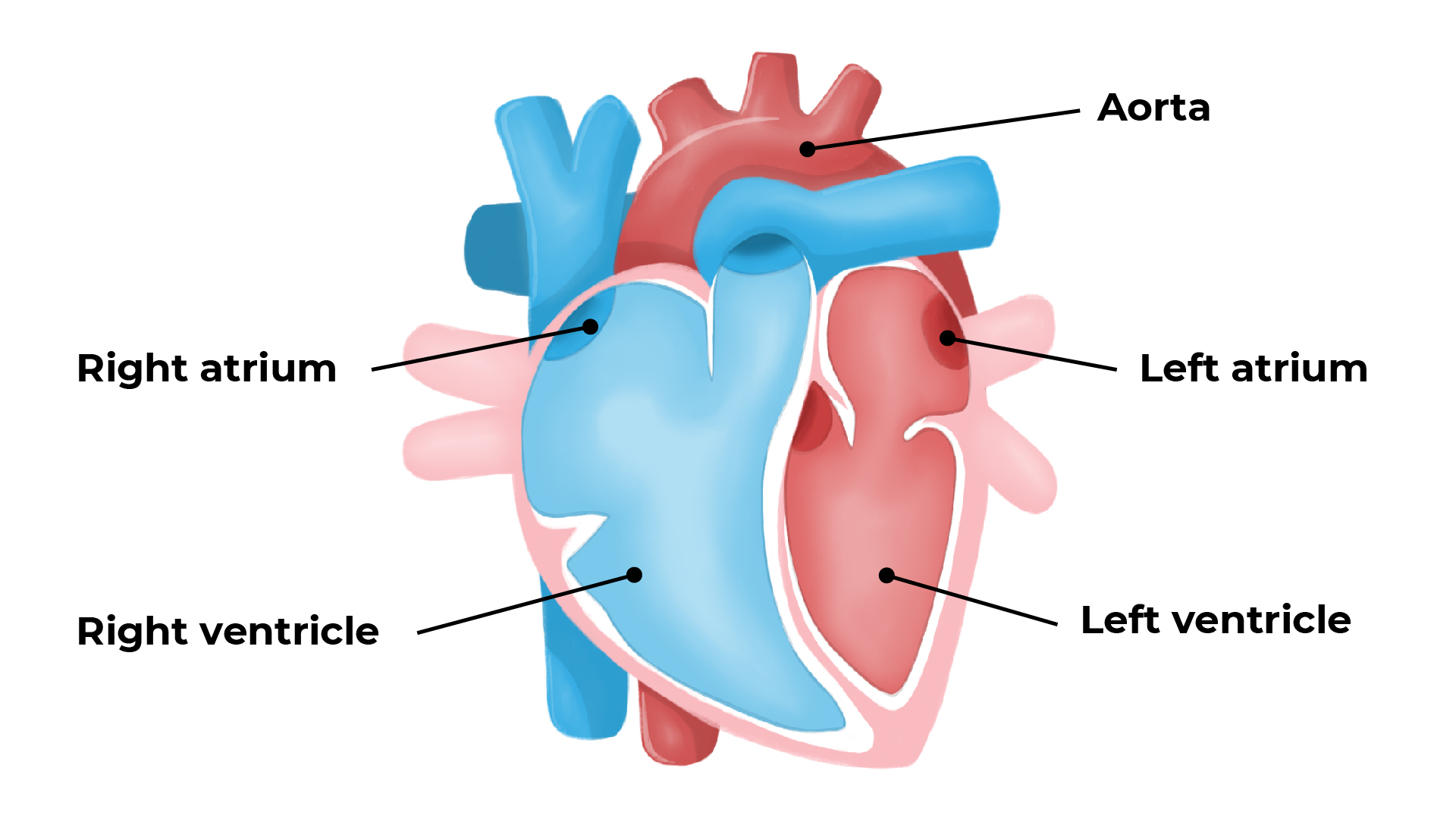
Parts of a heart

Diseases and the circulatory system:
Farm animals’ normal heart rates are seen in the table. Stress or disease changes the heart rate. The heart rate slows down as animals get older.
| Animals | Heart rate (beats/minute) |
| Cattle | 45-50 |
| Sheep | 70-80 |
| Pigs | 70-80 |
Anaemia - a shortage of haemoglobin which is the chemical in red blood cells that carries oxygen. This often arises if the animal is deficient in iron. It may be seen in young piglets whose diet is low in iron, and in ewes which have a heavy worm burden.
Cardiac failure - the heart stops pumping the blood around the body.
Conclusion
- Create questions for the following answers:
- Artery, capillaries, veins, lumen, haemoglobin, atrium, ventricle, aorta, vena cava, pulmonary artery, pulmonary vein, semi-lunar valves, bicuspid valve, tricuspid valve.