3. The Endocrine System
By the end of the session you will understand:
- The role played by hormones in controlling the body.
- The structure and function of the hypothalamus and pituitary gland.
- Structure and function of the pineal gland.
- Structure and function of the thymus and thyroid glands.
Starter:
- Individually, write down everything you know about hormones.
- Pair up to add to your ideas.
- The endocrine system produces hormones, that help the nervous system to control the body.
- The two systems are joined via the hypothalamus found in the brain.
- The gland produce the hormones and release them into the bloodstream to be carried around the body to affect their target tissues.
- Hormones work slowly and have a long-term effect (while nerves work very quickly for a very short time).
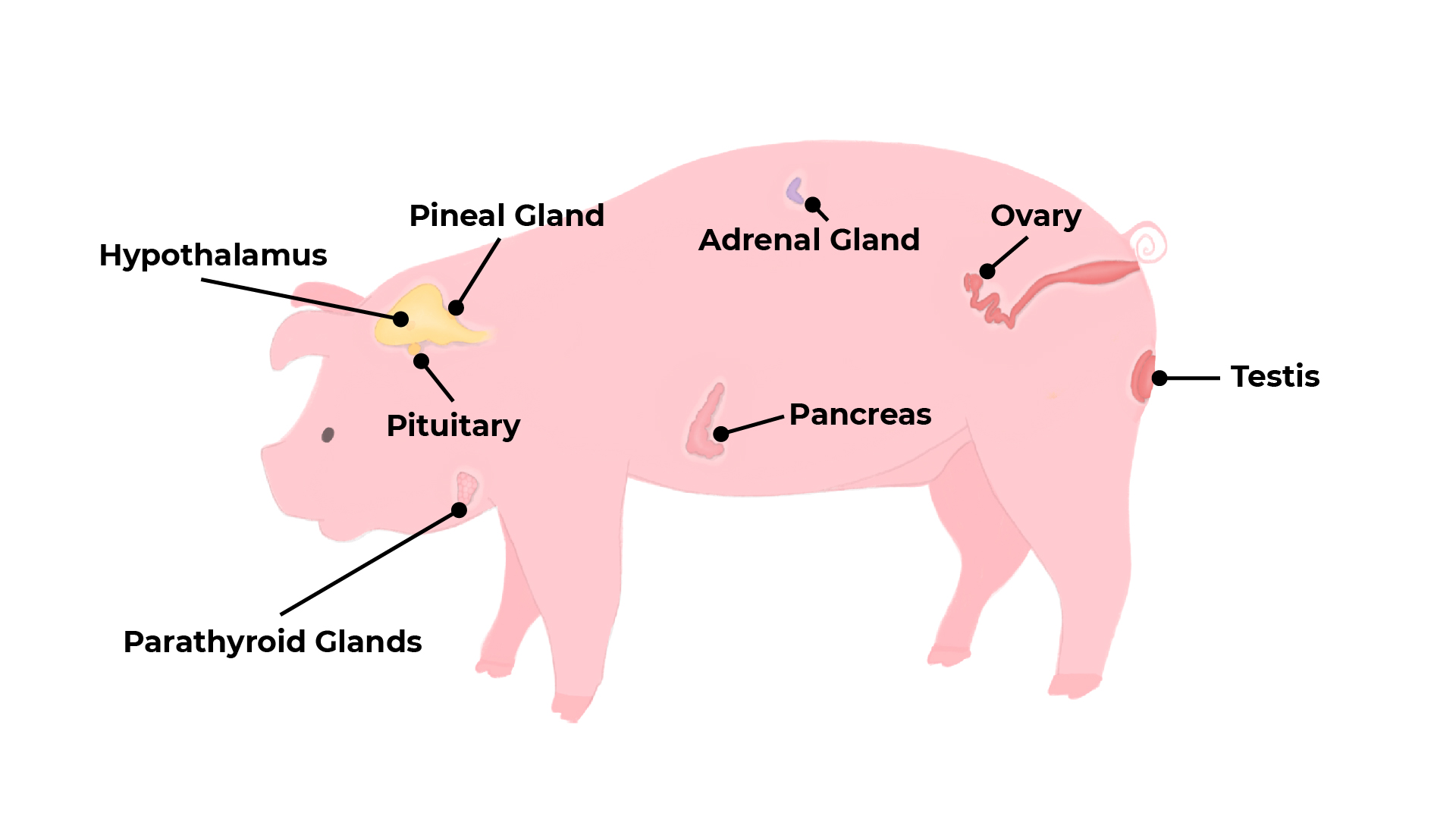
Endocrine Glands
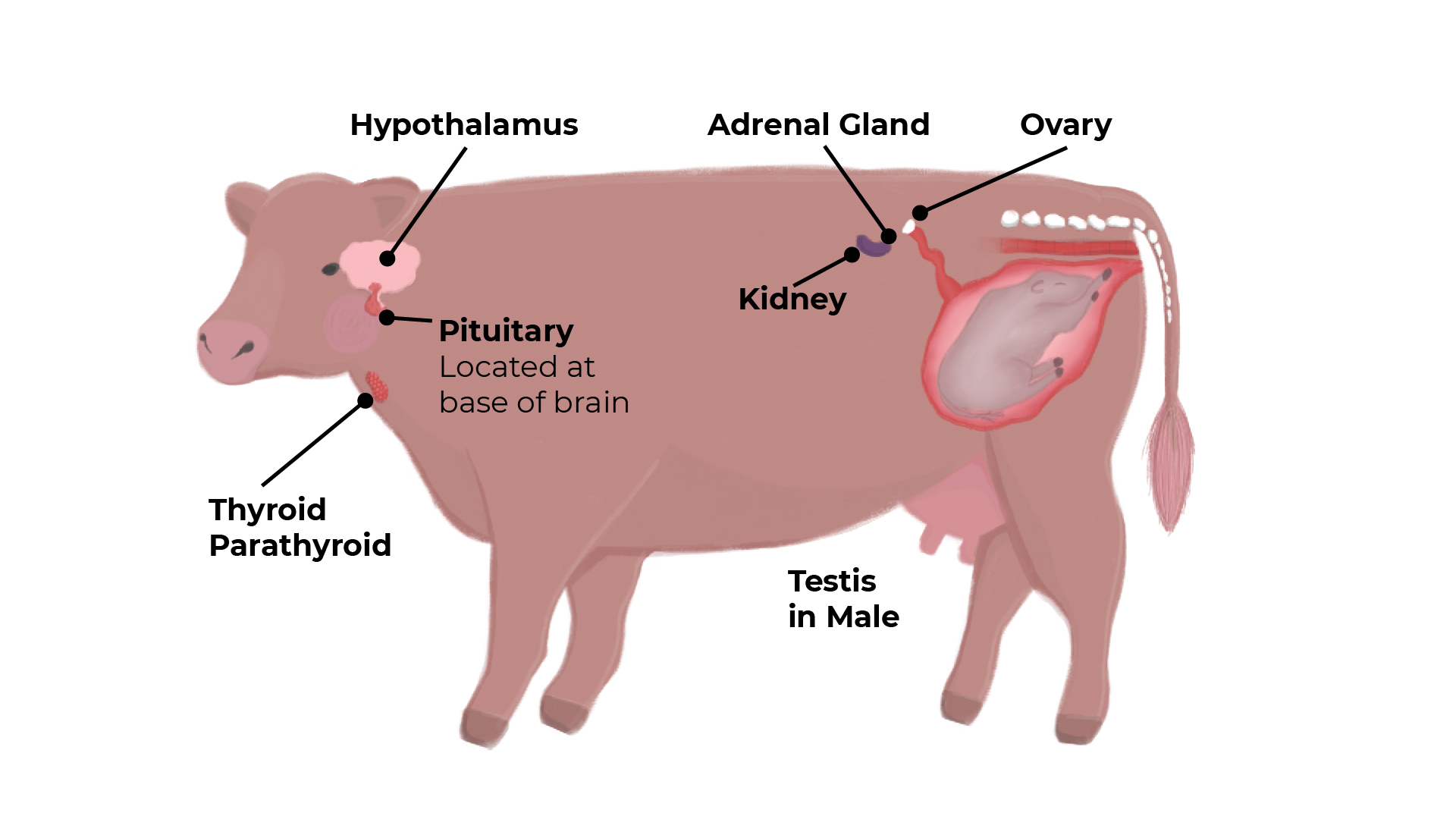
The Hypothalamus and the Pituitary Gland
The hypothalamus is found in the middle of the brain, with the pituitary gland hanging down from it.
The hypothalamus controls hormone release from the pituitary gland by producing, releasing or inhibiting hormones under the control of nervous impulses. The pituitary gland consists of the anterior and posterior parts.
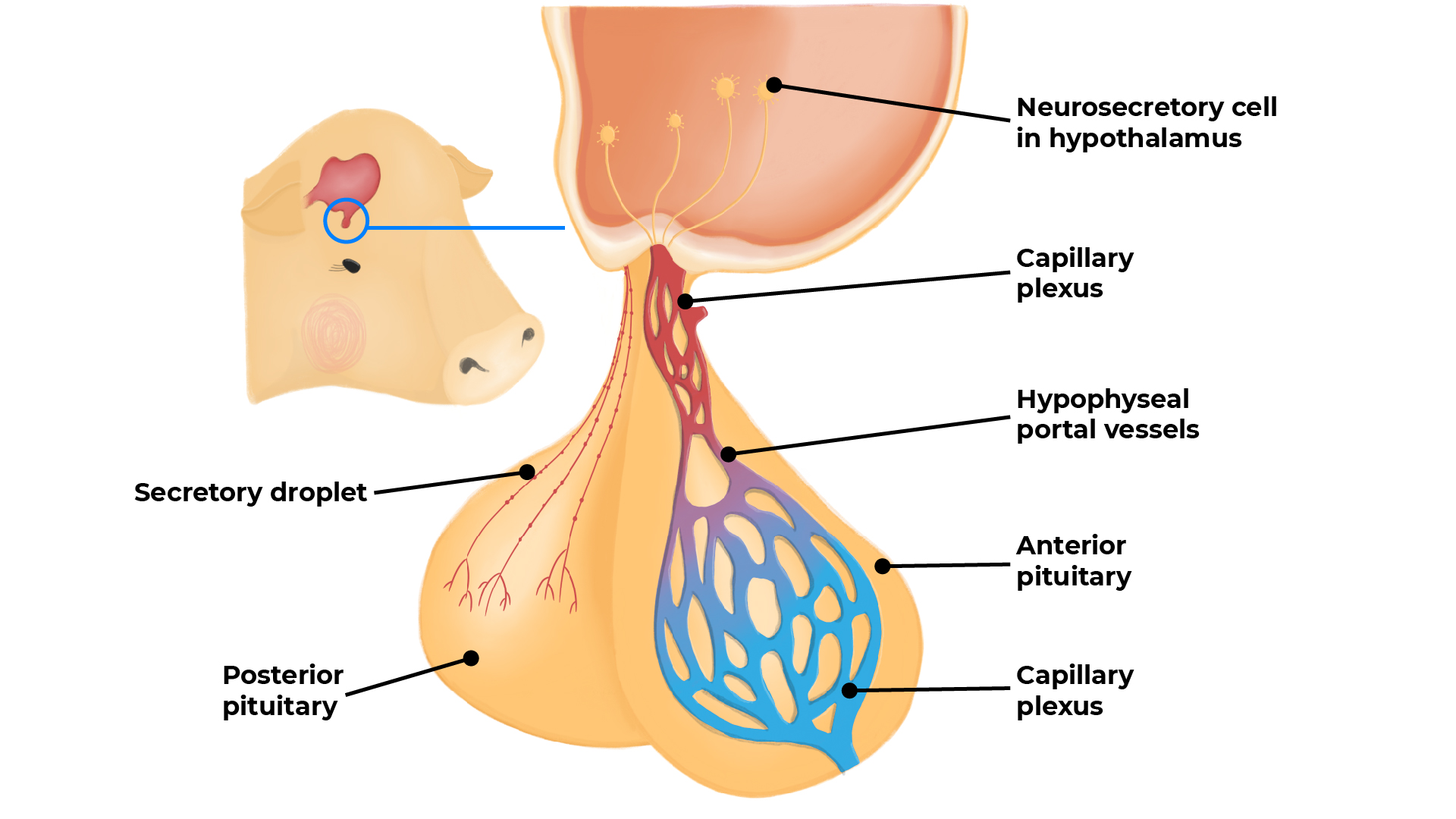
The pituitary gland’s hormones
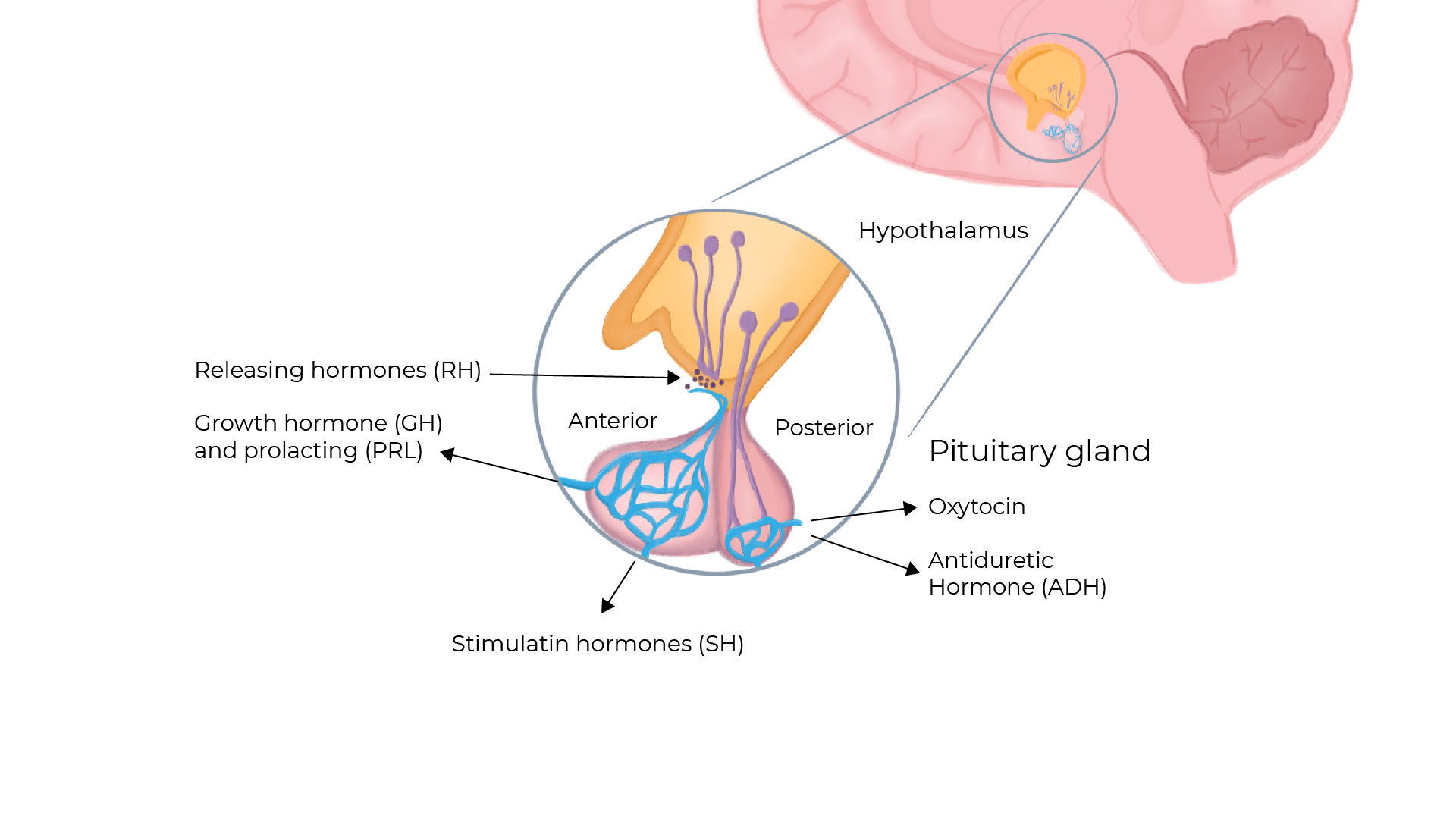
The pituitary gland’s hormones
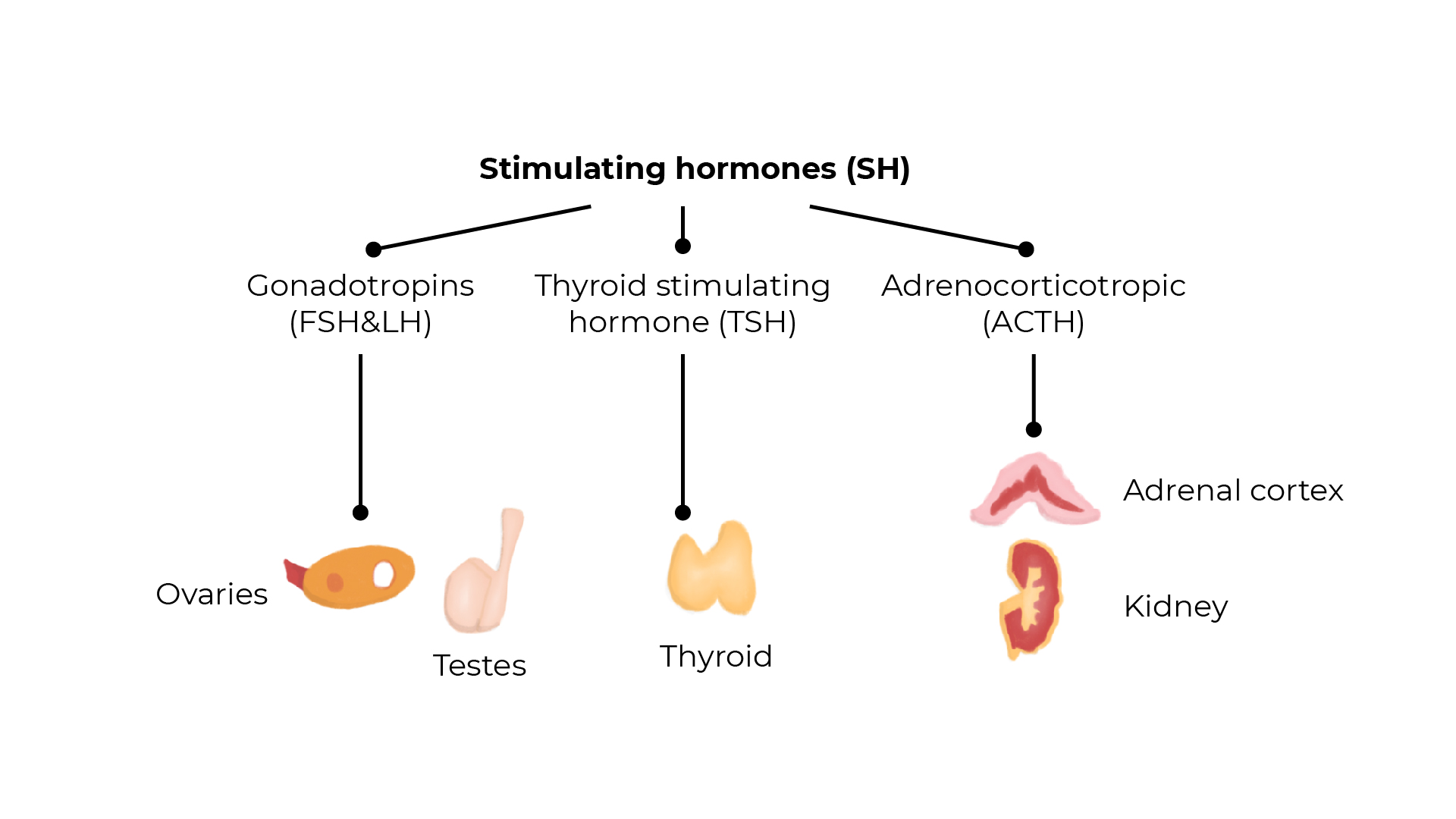
Look back at the paired list you created at the beginning of the topic. How much can you add to the list in one minute?
The thymus, thyroid and pineal glands
- Pineal gland
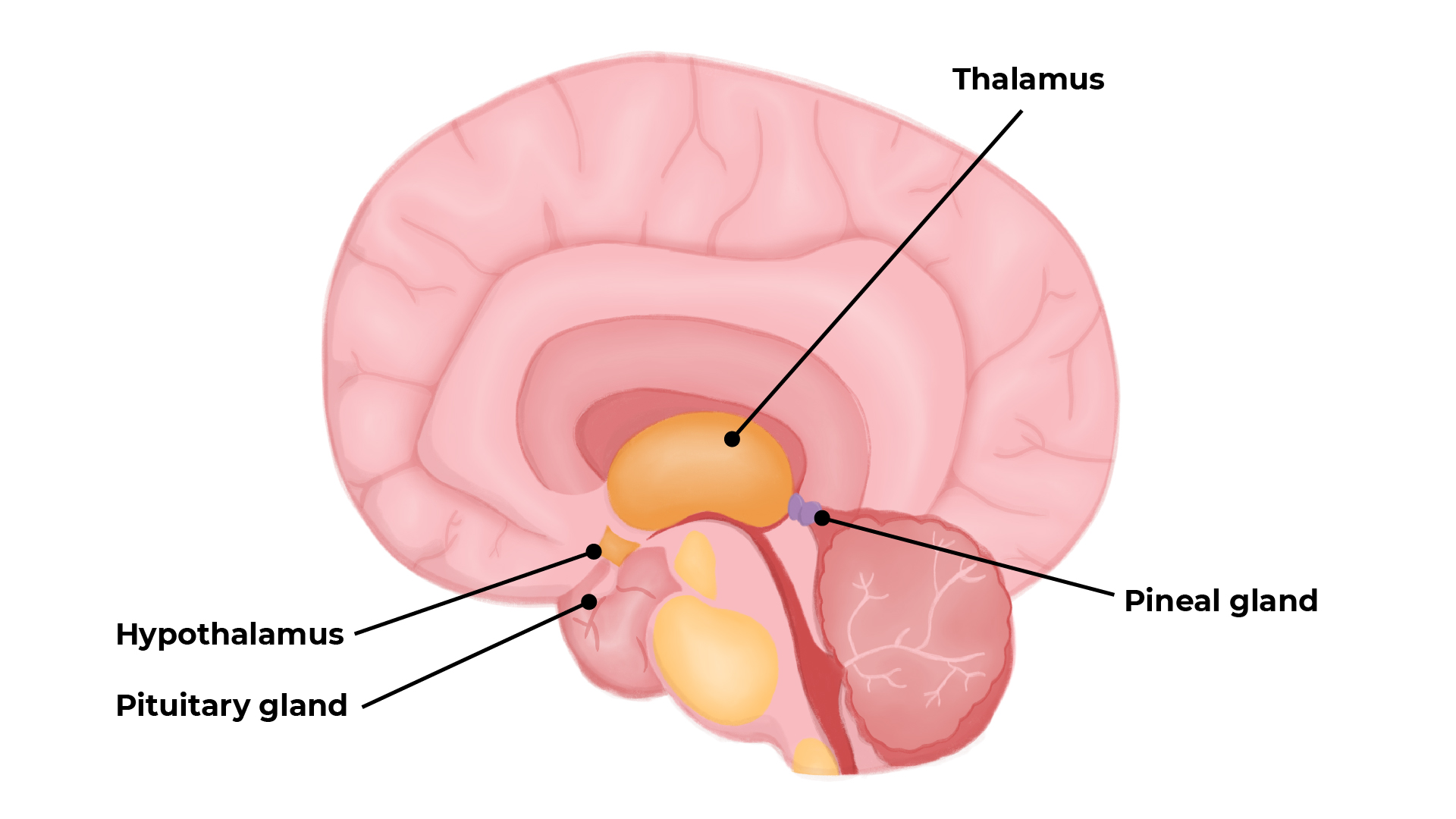
The pineal gland can sense the length of days. During darkness, the gland produces melatonin into the blood. As days shorten in autumn, melatonin levels in sheep's blood increase, causing sheep and rams to want to breed.
Sheep and rams can be implanted with melatonin to make lambing earlier, to get higher lamb prices.
The thymus and thyroid glands.
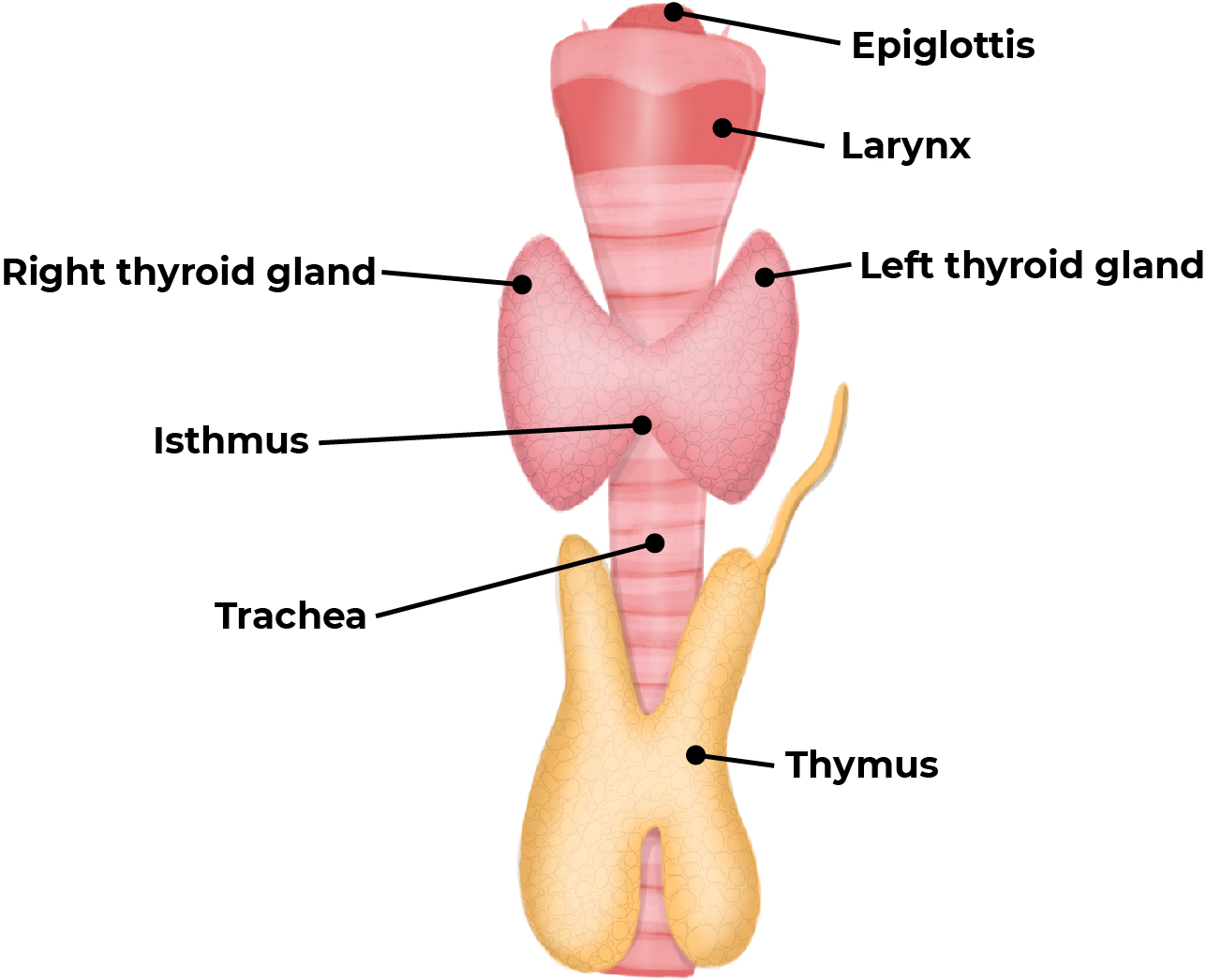
Thymus gland – part of the endocrine and immune systems. Produces and secretes the hormone thymosin which causes maturation and release of T cells from the thymus into the lymphatic system to fight against pathogens.
Thyroid gland – produces and releases the hormone thyroxine, which controls the body’s metabolic rate.
The pancreas and the adrenal gland
By the end of the session you will understand:
- the structure and function of the pancreas.
- the structure and function of the adrenal gland.
Pancreas
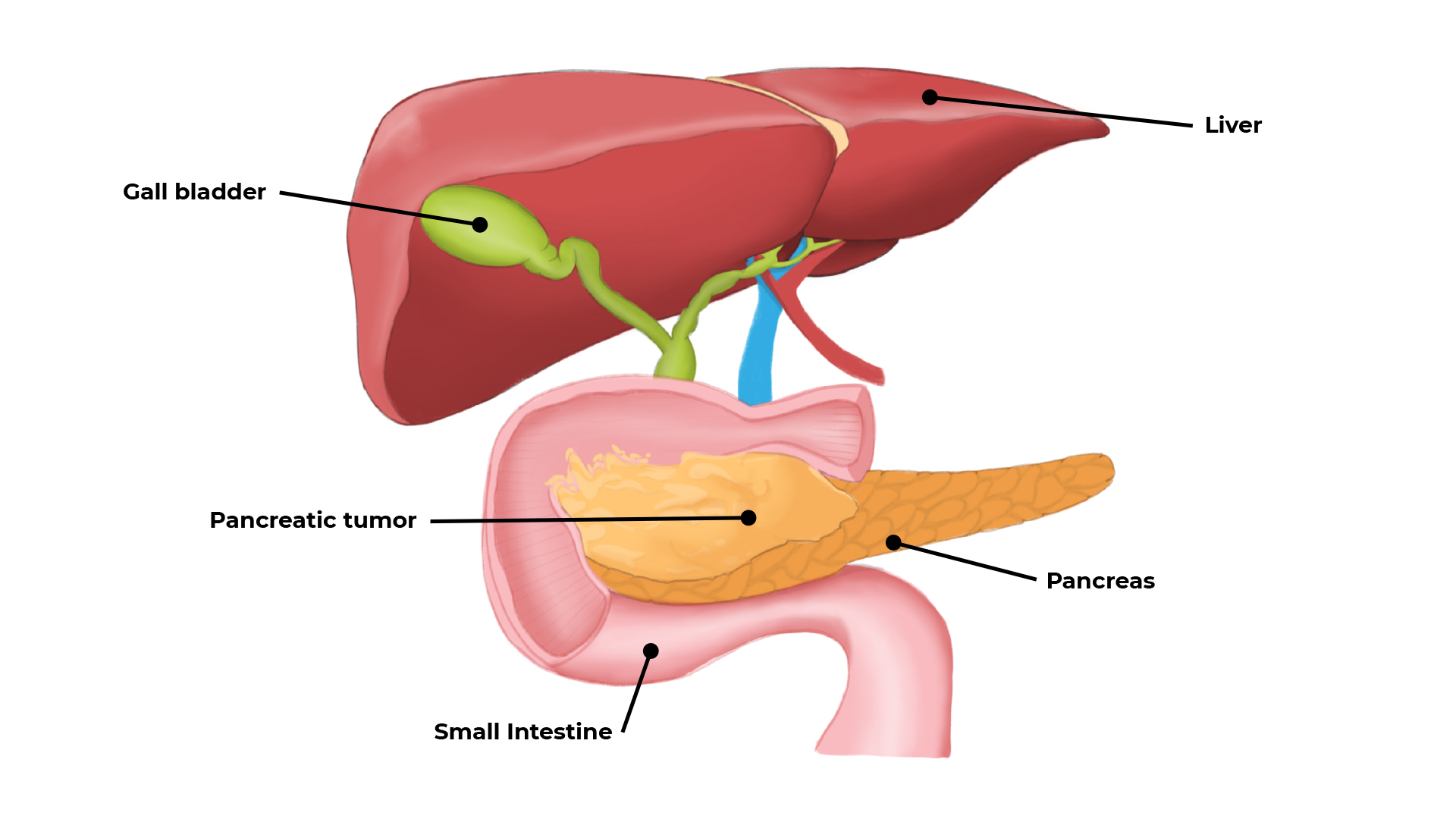
The pancreas controls glucose levels in the blood. The pancreas also produces the digestive enzymes. Insulin is produced by a group of cells in the pancreas.
Insulin
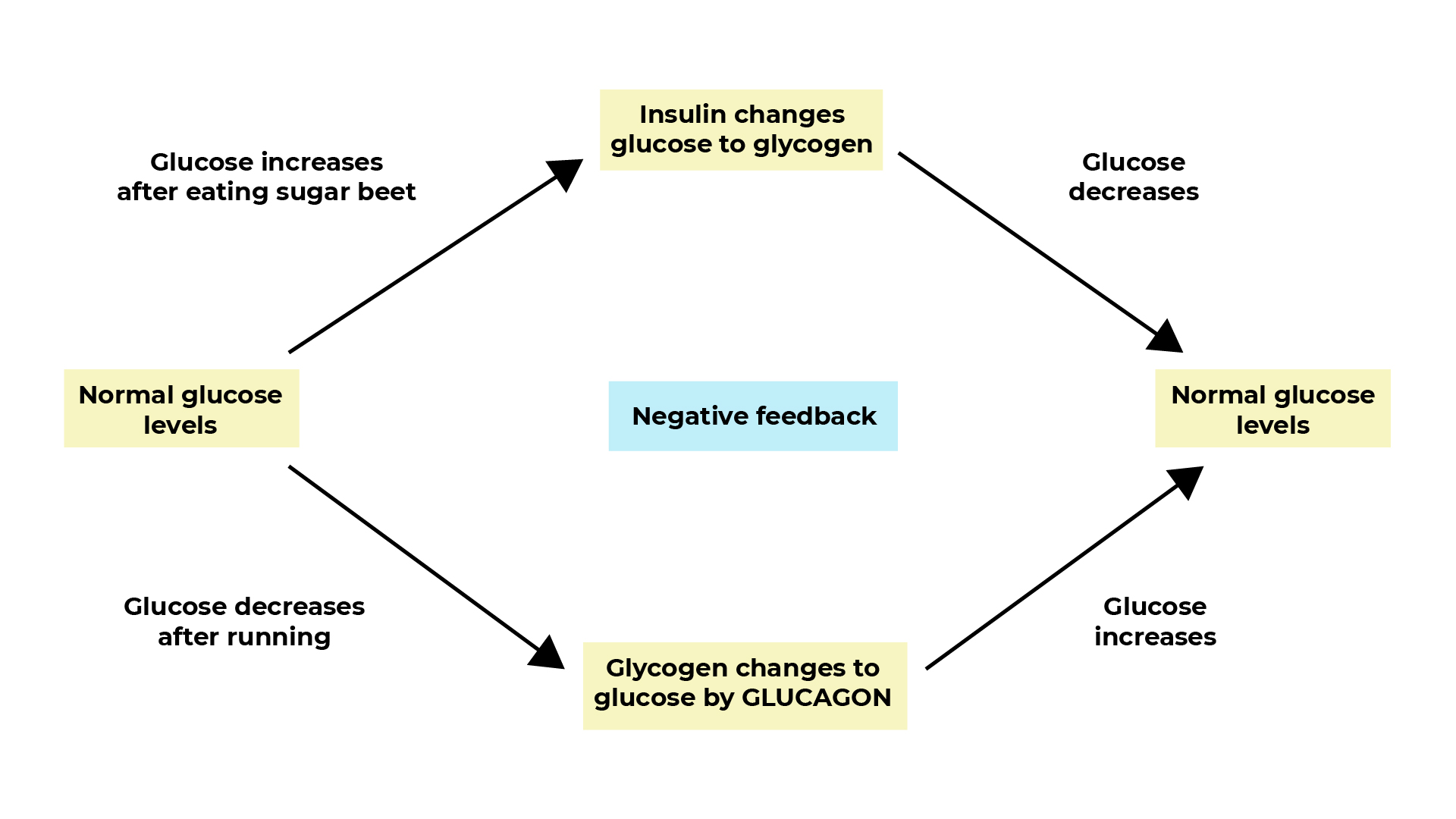
The hormone insulin controls glucose concentration in the blood. It keeps the glucose level in the body constant by homeostasis.
If there’s a increase in the blood glucose concentration:
- The pancreas produces insulin.
- Glucose is stored in the cells and liver as glycogen.
- Blood glucose concentration falls.
Lower concentration of glucose in the blood:
- Pancreas produces less insulin and more glucagon.
- Liver releases glucose into the blood.
- Blood glucose concentration increases.
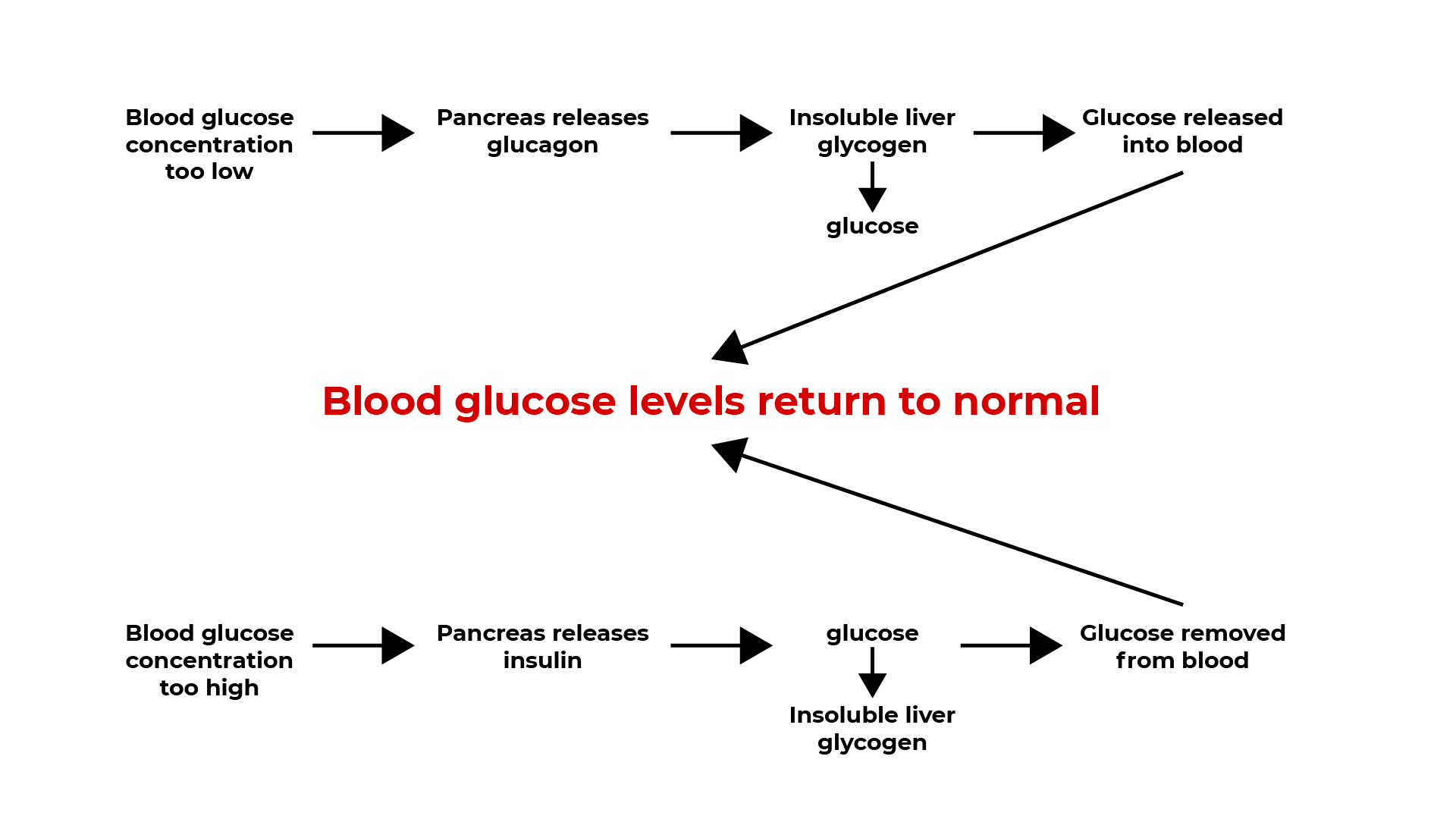
Controlling sugar levels
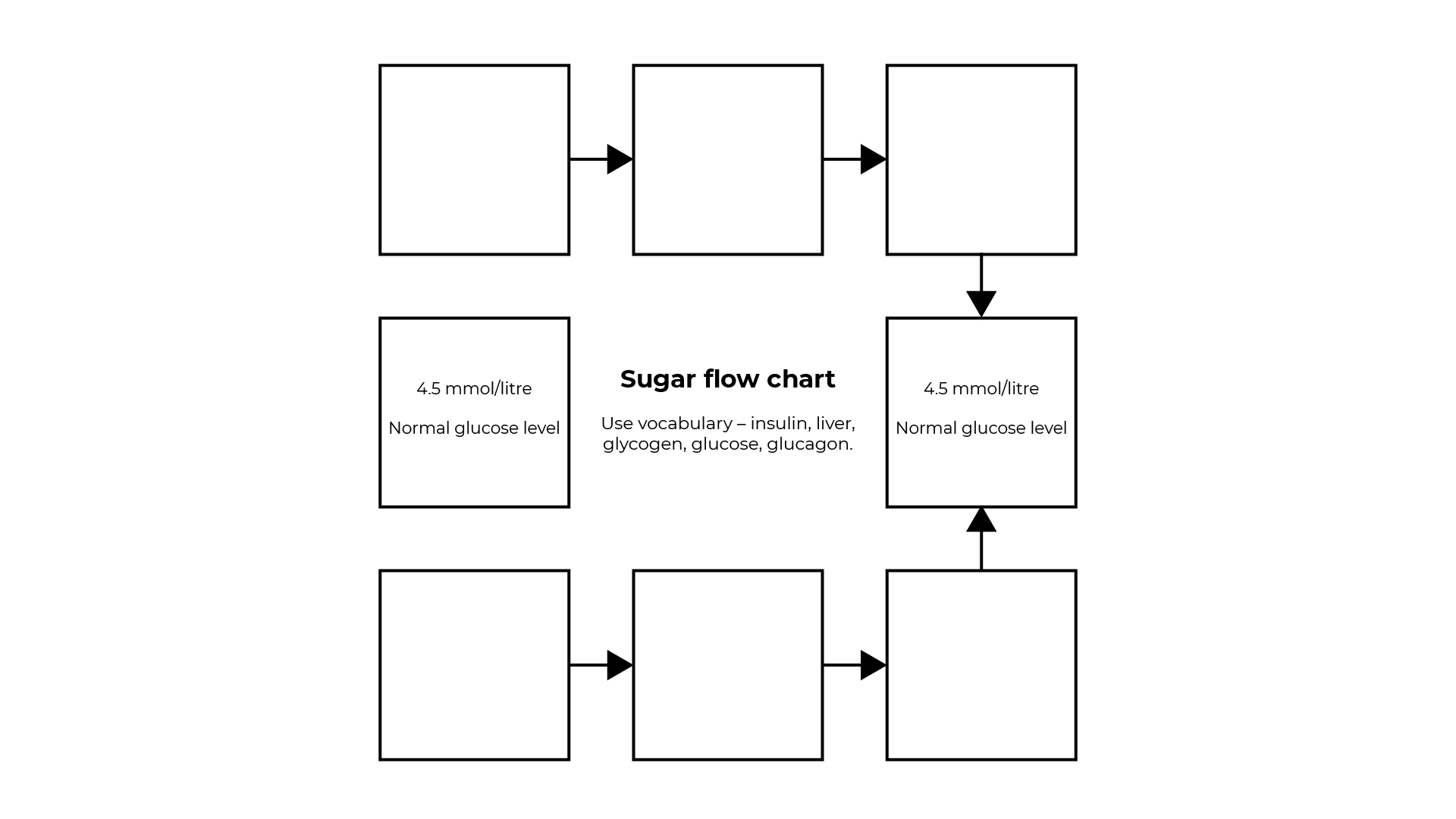
Complete the flow chart on next slide to show control of blood glucose levels.
Download - Word / PDF
The adrenal glands
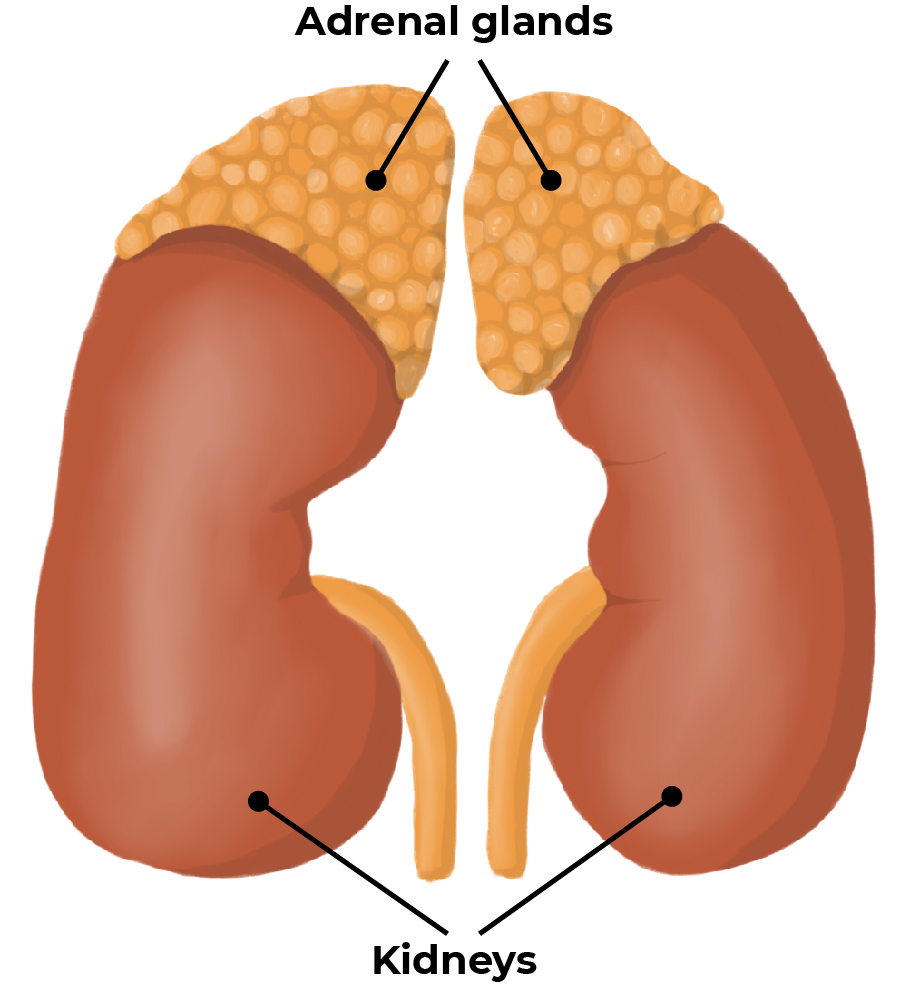
Adrenal glands – produce and secrete adrenalin that prepares the body for fight or flight.
Adrenalin causes the heart to beat faster, blood pressure to increase, breathing to deepen and get faster.
At the end of this session, you should now know:
- The role played by hormones in controlling the body.
- The structure and function of the hypothalamus and pituitary gland.
- The structure and function of the pineal gland.
- The structure and function of the thymus and thyroid glands.