Session 3:
Preparation, pre-start checks and common faults in machinery
Introduction
At the end of this session you will be able to:
- prepare selected land-based industry machinery for work in accordance with the manufacturers’ recommendations, user’s manual or machinery handbook.
- carry out pre-use checks for selected land-based industry machinery in accordance with the manufacturers’ recommendations, user’s manual or machinery handbook.
- identify common faults and suggest appropriate remedial action to the machinery.
- check and report on the safety requirements for selected land based industry machinery in accordance with the manufacturers’ recommendations, user’s manual or machinery handbook.
Prepare machinery for use
- Assess the job to be completed (suitability, access to fields, slopes, tyres).
- Check machinery is suitable and that you have the correct power input from the tractor (e.g. correct hp – horsepower).
- Check machinery has been serviced and that there are no repairs to be done.
- Check all safety devices in place and fit for purpose.
- Check that all oil levels are correct and that greasing has been done.
- Ensure machinery is safely and securely attached to the tractor.
- Ensure that the operator is familiar with the operating manual.
Personal pre-start checks
- Receive training before using any machinery.
- Suitable clothing – no loose clothing or jewellery which could get caught up in moving parts, tie back long hair, use suitable footwear (safety boots, clean with good grip) and PPE if required (ear defenders/gloves).
- Be alert and not overtired.
- Be familiar with the controls and capability of the tractor.
Pre-start checks on tractors and machinery
- Check fuel – either a visual check in older models or check the fuel gauge.
- Check oil – gear box /power steering /engine /rear axle.
- Clutch and brake fluid.
- Check water level and radiator is free from debris.
- Check tyres for wear/pressure and defects.
- Check lights especially brake, indicator and beacon.
- Check battery connections and electrolyte level.
- Check fan belt for tension and wear.
- Check all windows are clean.
- Check mirrors are in the correct position and clean.
Identifying common faults in land-based machinery
There can be a variety of faults that can occur in the working day/life of a machine.
- incorrect, polluted or lack of fuel
- blocked filters (air, fuel, oils)
- poor oil pressure
- damaged sprockets and fouled drive systems
- damaged or blunt blades
- fouled or incorrectly set gap of spark plugs
- starter recoil tension
- blocked mechanisms
All of these would cause the machine to work less effectively or to break down.
What are the safety requirements for selected land-based industry machinery?
Theses are usually found in the:
- manufacturers’ recommendations when they sell a machine to a farmer
- user’s manual
- machinery handbook
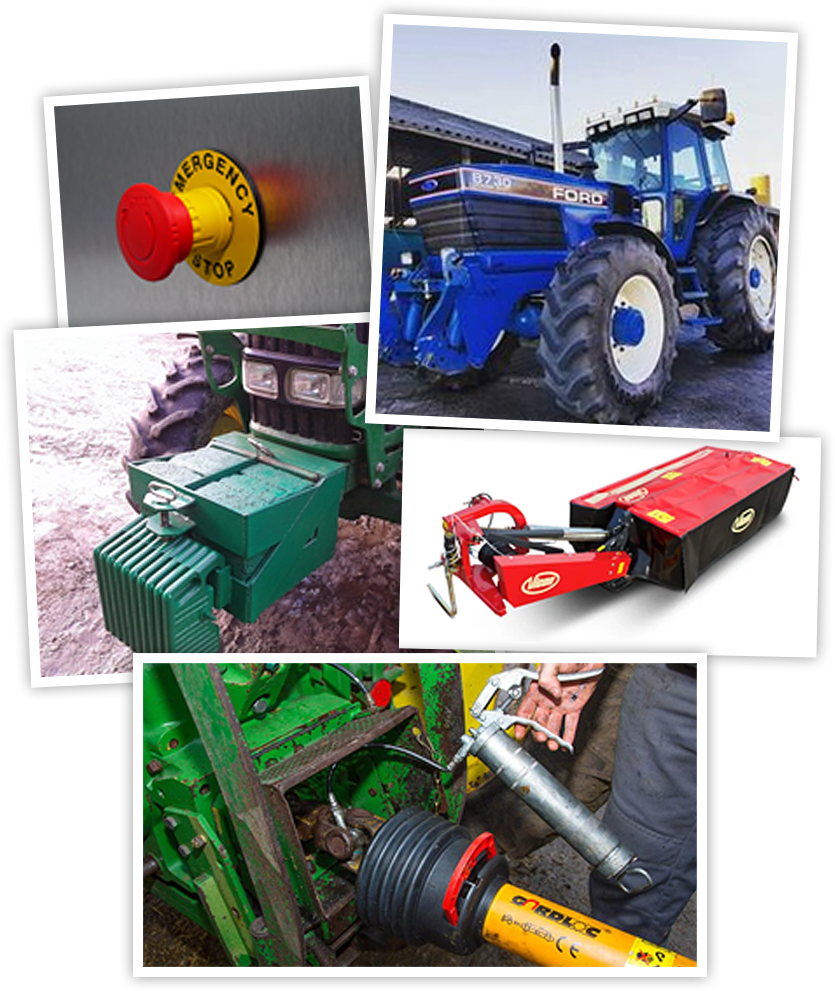
Examples of safety requirements on machines
- safety cab
- PTO guards
- blades/knives guards
- emergency stop buttons
- ridged/serrated step up to tractor cab
- ballast for balance to avoid tipping

Conclusion
At the end of this session and after a series of practical tasks in the workshop and in the field you should be able to:
- prepare selected land-based industry machinery for work.
- carry out pre-use checks for selected land-based industry machinery.
- identify common faults and suggest appropriate remedial action to the machinery.
- check and report on the safety requirements for selected land-based industry.