Session 6:
Introduction to Lifting and Cutting Equipment:
Mowers, Conditioners, Tedders & Rakes
Aim of the session:
At the end of this session, you will be able to:
- give examples of different types of mowers.
- describe how mowers work.
- explain how the mowers operate.
Note:
Before operation of any machine make sure you familiarise yourself with the following.
- Risk assessment
- Adherence to industry safety guidance and operator’s manual
- Safe start and stop
- Monitoring of machine performance and output
- Effective communications
- Clearance of blockages
- Conversion between work and transport positions
- Economic operation
- Safe and efficient operation
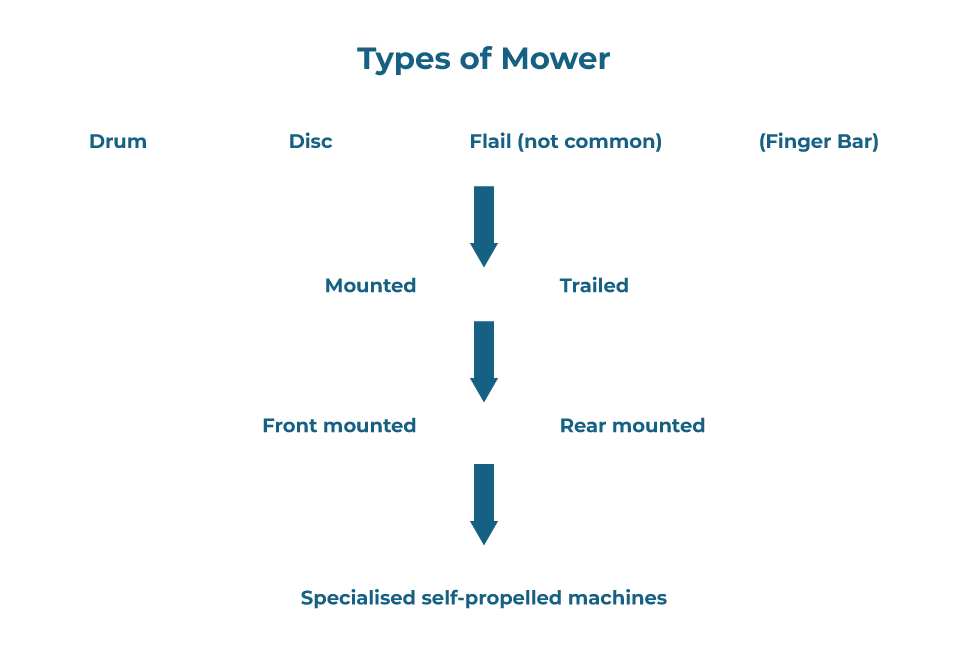
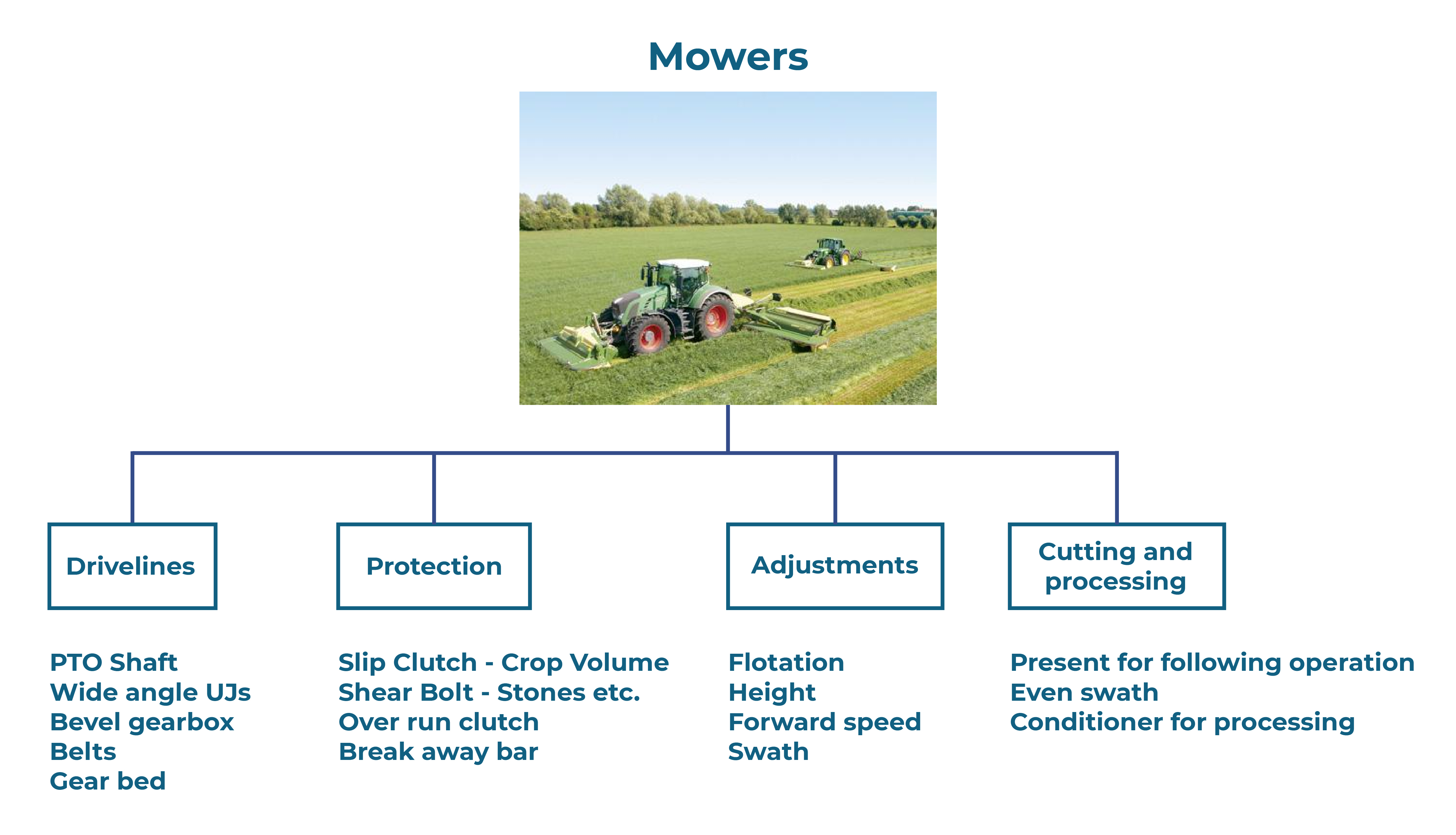
Mowers
Function
To cut grass of varying type, length and condition, then present it for further operations, e.g.
- tedding
- rows (raking)
- picking up by forage harvester, etc.
Mowers

- Swath – A line or row of cut grass thrown together by the machine.
- For many years, mowers were of the cutter bar type. However, these machines have now been replaced by rotary mowers and to a lesser extent, the flail mower.
Cutter Bar Mower
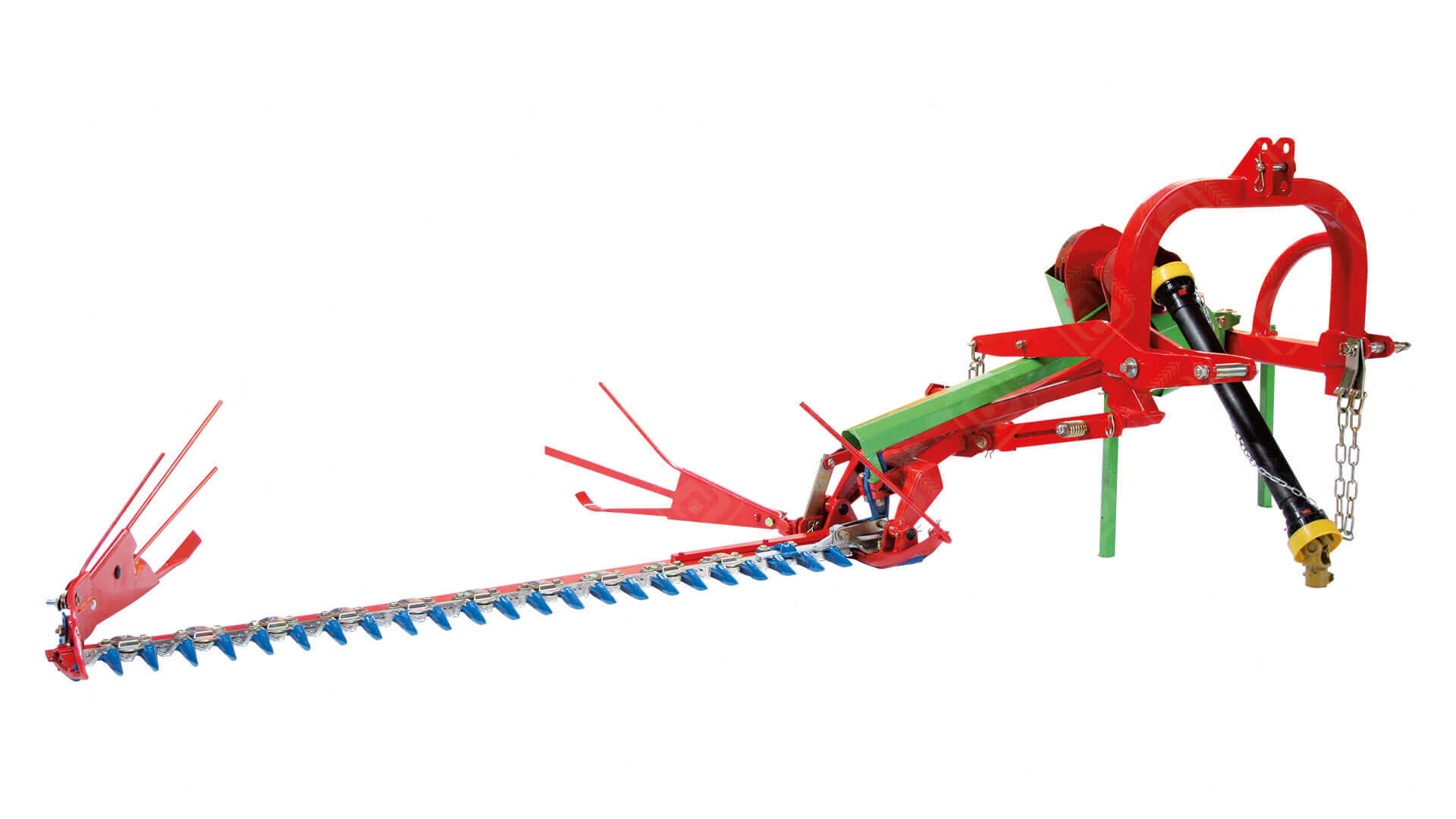

- The reciprocating knife cutting mechanism is similar to that of a combine harvester.
- The knife is driven by the power take off through a crank and pitman (connecting rod).
- The drive crank runs at approx 500rpm giving about 1,000 cutting strokes per minute.
- The knife stroke is 75mm and safety devices include a cutter bar break back mechanism, slip clutch in the main drive and the drive belts.
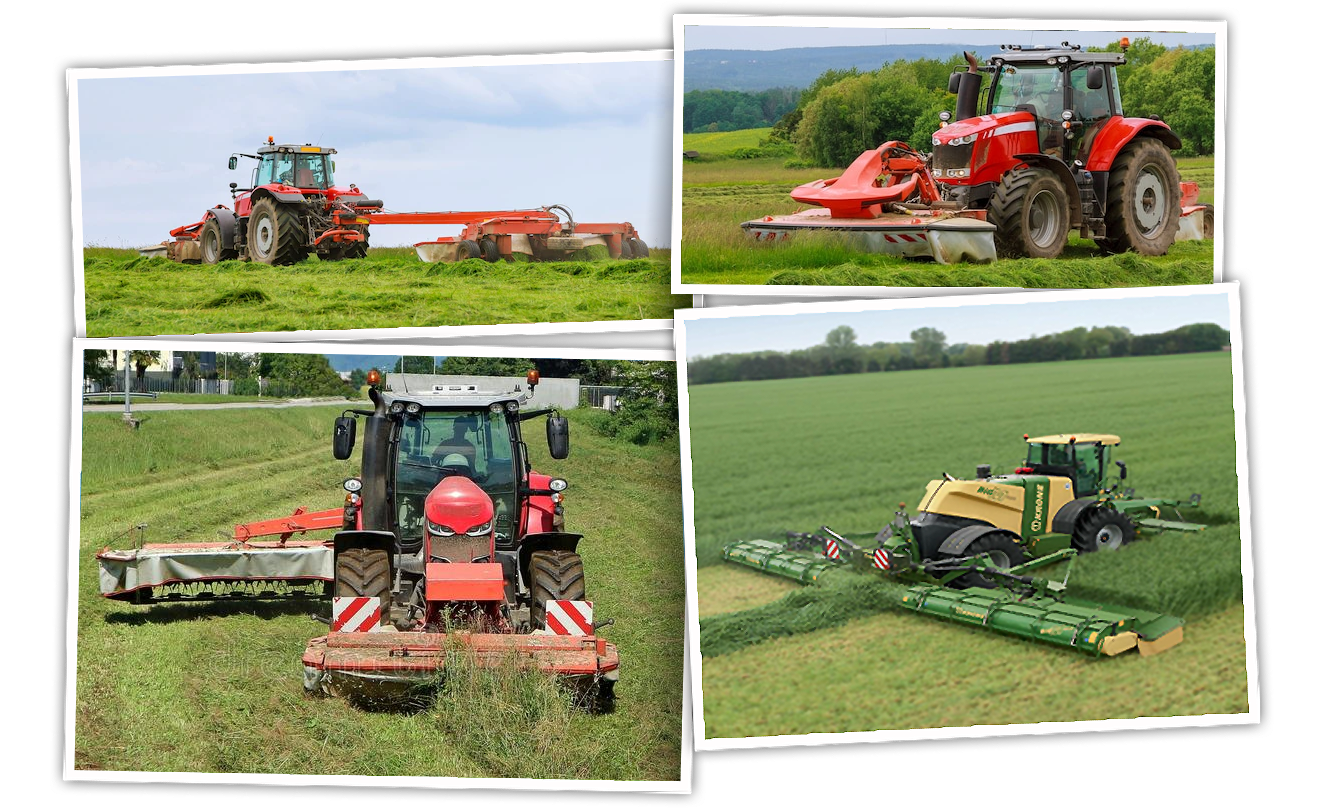
Rotary Mower
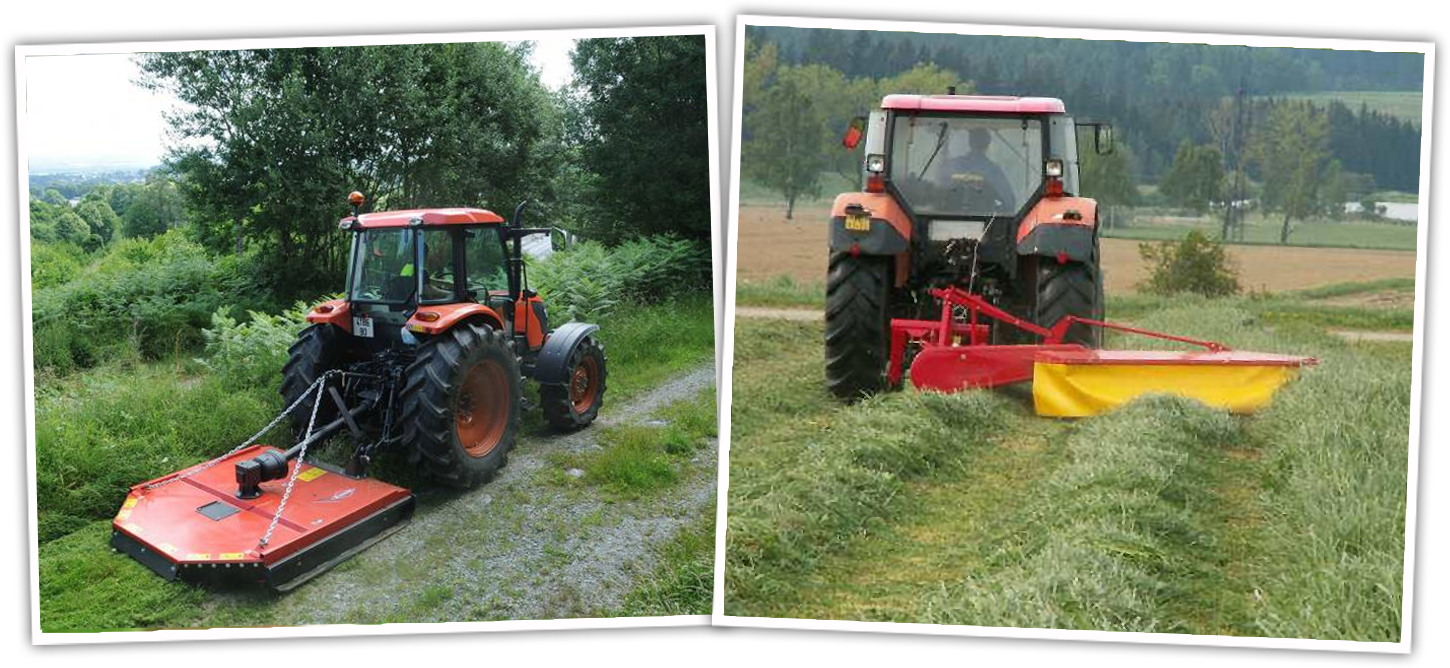

- Rotary mowers have a high work rate and a relative freedom from blockages, even in heavy or tangled crops.
- Working speeds of up to 15km/h can be achieved in good working conditions.
- Either mounted on a three-point linkage, or trailed and are driven by the power take off.
- Some are front mounted, leaving the rear linkage free for mounting a second offset mower.
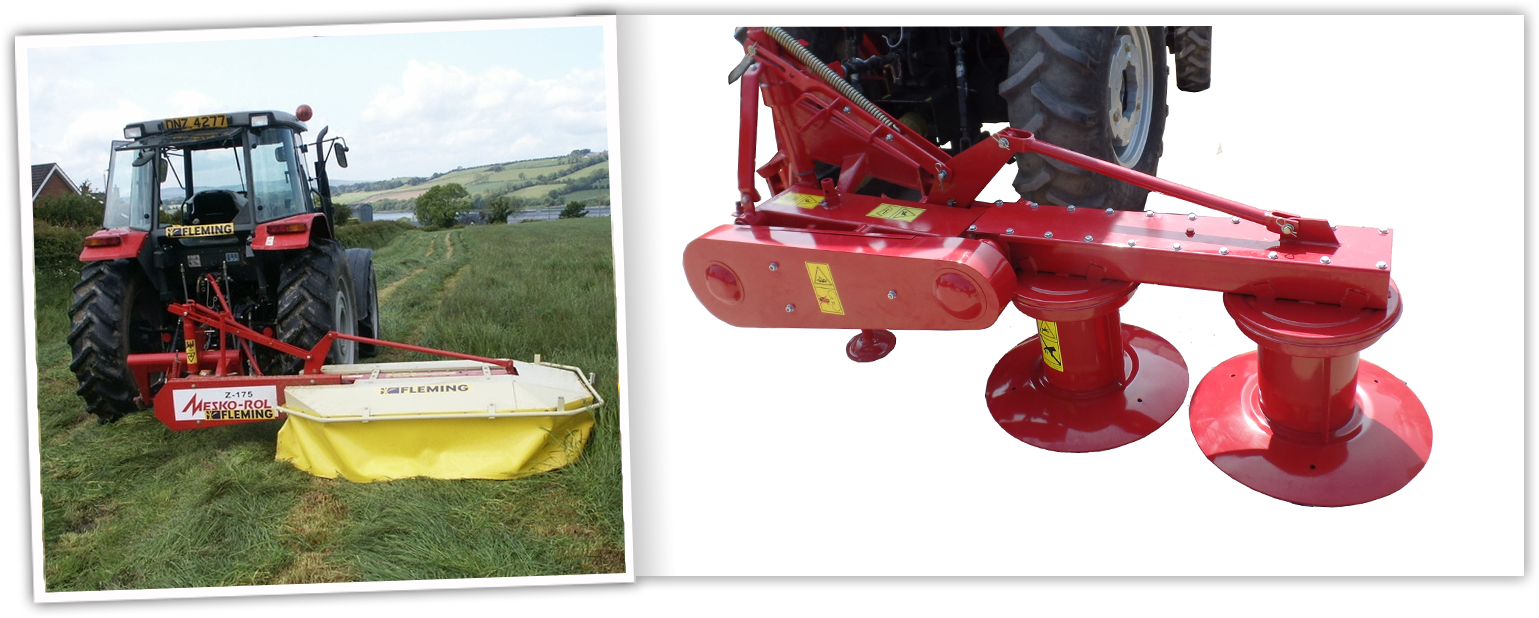

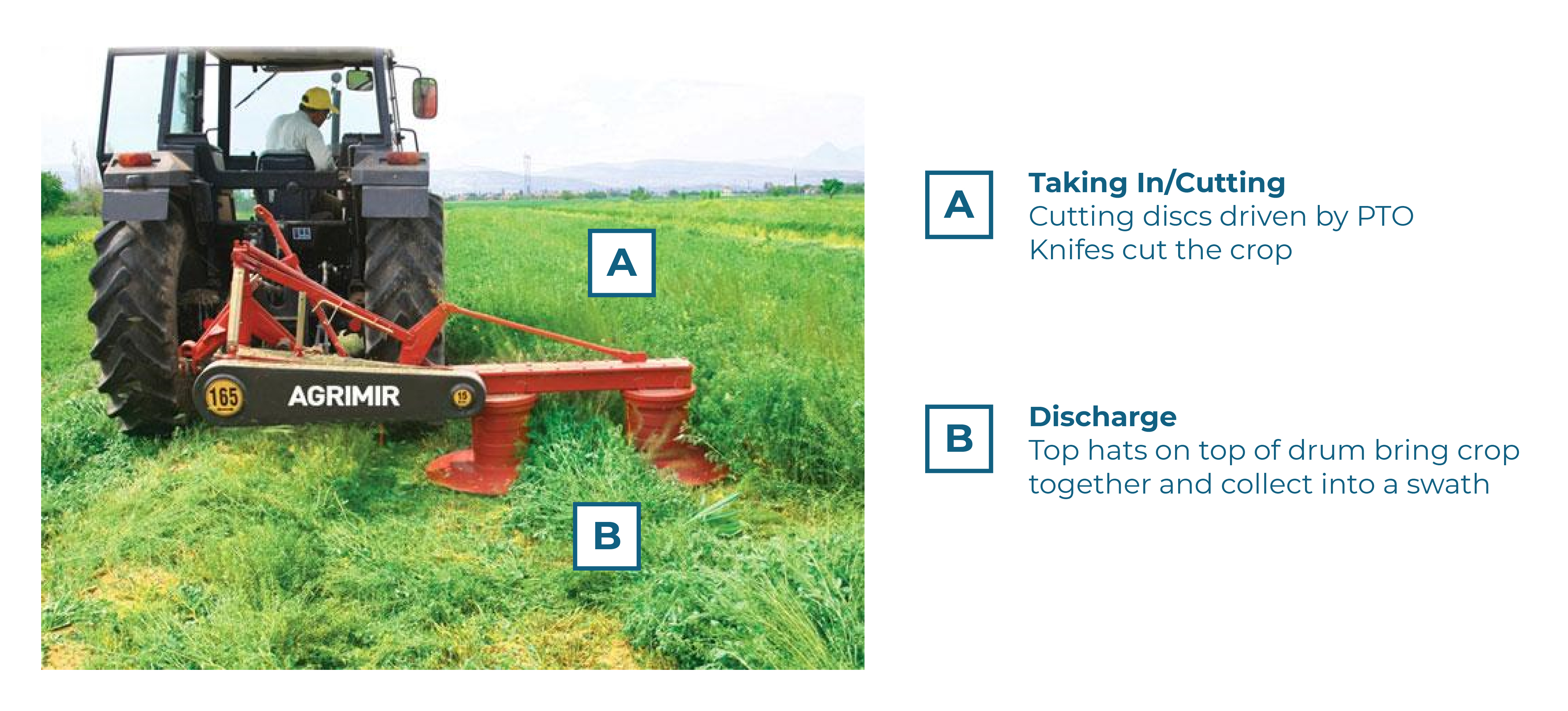
Drum Mowers
Contra-rotating drums with free-swinging knives cut the crop and eject a swath rearward from the machine.
- two, three or four drums
- trailed, mounted or front mounted
- with or without conditioner
- working widths 1.65 to 4m
- drums rotate at 1600 to 1800 rpm
- 3 or 4 knives per drum
- knife tip speed is approximately 70m/sec (170 mph)
- cutting / stubble height 20 to 100 mm
- height adjusted by different knives, skids under drums, moveable drums, stops on lifting, support rams
- floatation linkage allows machine to follow ground contours
- driveline protected by slip clutches, over run clutches, shearbolts and belts (slippage)
At the end of the session, you are now able to:
- give examples of different types of agricultural mowers.
- describe and explain how mowers operate.